4 Window Ratings You Should Know

Window rating labels can be confusing for the average consumer. But to know that you’re getting the right, energy-efficient windows for your home, it’s imperative to understand what they mean.
If you want to become a more educated consumer, understanding the four standard energy ratings on your window labels is a great place to start.
These four common energy ratings will help you understand how energy-efficient your windows are. There are countless benefits to getting new energy-efficient windows, such as lowering your heating and cooling costs and reducing your carbon footprint. And, you could even qualify for a tax credit of up to $3,200 by switching to energy-efficient windows.
If you want to learn more about your window ratings, keep reading as we explain each one.
Look for the NFRC Label
When buying new home windows, look for a company with NFRC Certified windows. The National Fenestration Rating Council (shortened as NFRC) conducts extensive independent testing on windows and labels them with the ratings you see.
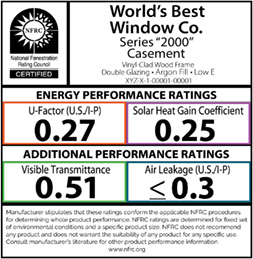
This is what an NFRC label looks like (Source: nfrc.org).
The Difference Between the NFRC Label and ENERGY STAR
You may be familiar with the ENERGY STAR label. Windows that are ENERGY STAR certified are officially deemed as energy-efficient products. So, if your primary concern is to look for energy-efficient windows, why would you need to look for the NFRC label, too?
The answer lies in the difference between these two labels. ENERGY STAR labels show that a product is certified as energy efficient, whereas the NFRC label offers individual ratings for each specific window. This allows you to compare two windows, seeing which is more energy efficient.
Now that we’ve covered the basics, let’s get into what each rating on the NFRC label means.
U-Factor
In simple terms, the U-Factor determines how well-insulated a window is. This number measures how well the window can prevent heat from escaping a room. U-Factors range from 0.20-1.20; the lower the number, the better.
Solar Heat Gain Coefficient
The Solar Heat Gain Coefficient measures how much a window can resist unwanted heat gain, which is essential in summer and hotter climates where room temperatures could increase. The lower the number, the less unwanted heat your home will have. This rating ranges from 0-1; the lower the number, the better. Having windows with low SHGCs can ultimately lower your cooling costs!
Visible Transmittance
Visible Transmittance measures how much daylight filters into your home through your windows. This rating is worth looking at because more daylight reduces the need for artificial lighting, ultimately saving you money on electricity. The higher this number, the more light is let into your home. This rating ranges from 0-1, so look for higher numbers.
Air Leakage
Lastly, air leakage measures how much air can get in through the windows. Obviously, you want less air leakage in your home to prevent drafts and unwanted temperature changes. Look for a rating that is less than or equal to 0.3.
Find the Perfect, Energy-Efficient Windows for You
If you’re looking for ENERGY STAR certified and NFRC Certified windows, look no further than Earthwise Windows.
Our certifications prove that we are one of the top energy-efficient window manufacturers in the United States. Our windows are made by regional manufacturers, so they’re built to perform for your specific climate.
Reach out to an Earthwise specialist near you today to get a quote on new, energy-efficient home windows.
Source:
“Energy Performance Label: National Fenestration Rating Council.” National Fenestration Rating Council, 11 July 2022, www.nfrc.org/energy-performance-label/.
Did you find this info useful? It's ok to share:






